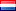
3-Step+ charging
This modern charging technology allows a battery to be quickly and safely charged in three phases (steps).
The first step is the bulk phase, in which the battery is charged quickly. The output current of the battery charger is at maximum (100 %) during this phase and the battery voltage depends on the charging degree of the battery. The duration of this phase depends on the ratio of battery to charger capacity, and on the degree to which the batteries were discharged to begin with.
The bulk phase is followed by the absorption phase, which begins once a battery has been charged to ± 80 % (90 % for Gel and AGM batteries), and ends when the battery is completely full. Battery voltage remains constant throughout this stage, and the charging current depends on the degree to which the battery was initially discharged, the battery type, the ambient temperature, and so on. With a flooded battery this phase lasts some four hours, with Gel and AGM batteries around three. This does not apply to Lithium Ion batteries as these are charged to 100 % with full current.
Once the battery is 100 % charged, the Mastervolt charger automatically switches to the float phase. In this step, the batteries are kept in optimal condition and the connected users are supplied with power. If power consumption is higher than can be supplied by the battery charger, the remaining power is supplied by the battery. The battery is then (partly) discharged and the charger automatically switches back to the bulk phase. If consumption is reduced, the charger will start charging the battery again via 3-step+ charging. A battery charger with 3-step+ charging can remain connected to the battery, even in winter, and ensures a long lifespan for your batteries as well as being safe for the connected equipment.
Absorption time
The duration of the second phase in the charging of a battery. The battery will, in general, be charged from 80 to 100 % during this phase, which lasts around four hours with a flooded lead battery, and three hours with Gel and AGM batteries. With Lithium Ion batteries the absorption time is very short as they can be charged to 100 % with full current. This phase is automatically set for Mastervolt battery chargers.
3-Step+ charging characteristic (IUoUo)

Charge factor
The charge factor indicates the efficiency of a battery. The efficiency of the average flooded battery is approx. 80 %, which means it must be recharged 1.2 times the eventual capacity in Ah to get the same capacity. This translates into a charge factor of 1.2. The lower the charge factor or the higher the battery efficiency, the better the quality. Mastervolt’s Gel and AGM batteries have an efficiency of > 90 % and a low charge factor of 1.1 to 1.15 and offer the very best quality.
Discharge factor
This is also known as Peukert’s Law, and allows you to determine how long a battery can be used at a given load before it needs recharging.
Cycle
A battery only lasts a certain number of charge/discharge cycles, depending on its type and quality. In theory one charge/discharge cycle is the process of discharging a battery to 0 % of capacity and recharging it back to 100 %. Twice recharging after discharging to 50 % is also one cycle, as is four times discharging to 75 % and recharging. A starter battery, for instance, can take around 50 to 80 cycles, which may seem little but is in practice more than sufficient: While the current used for starting an engine is high, it only lasts a short time and represents 0.001 of a cycle. In other words, an engine can be started 80,000 times before a battery is worn out. A high-quality semi-traction battery lasts for around 250 to 300 cycles. If the battery is only discharged to 50 % of capacity, 600 cycles are available. Assuming 25 weekends of use (50 days) plus 20 days of holiday and discharging only to 50 %, the battery will go through 70 half cycles or 35 full cycles.